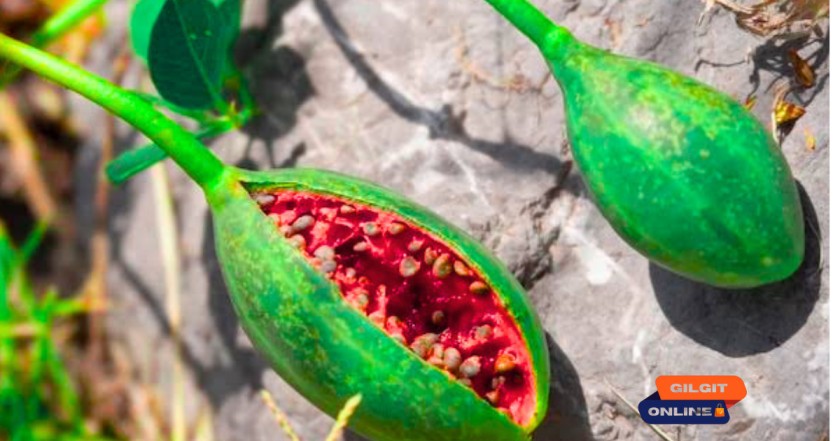
Capparis spinosa, commonly known as caper bush, is a fascinating perennial plant known for its culinary and medicinal uses. While it is native to the Mediterranean and parts of Asia, the Himalayan variety of Capparis spinosa thrives in rugged, high-altitude regions, offering unique health benefits.
In this SEO-optimized blog post, we’ll explore:
✔ What is Capparis spinosa?
✔ Nutritional and medicinal benefits
✔ Culinary uses of capers
✔ How to grow Himalayan Capparis spinosa
✔ Traditional uses in Ayurveda and folk medicine
By the end, you’ll understand why this plant is cherished worldwide!
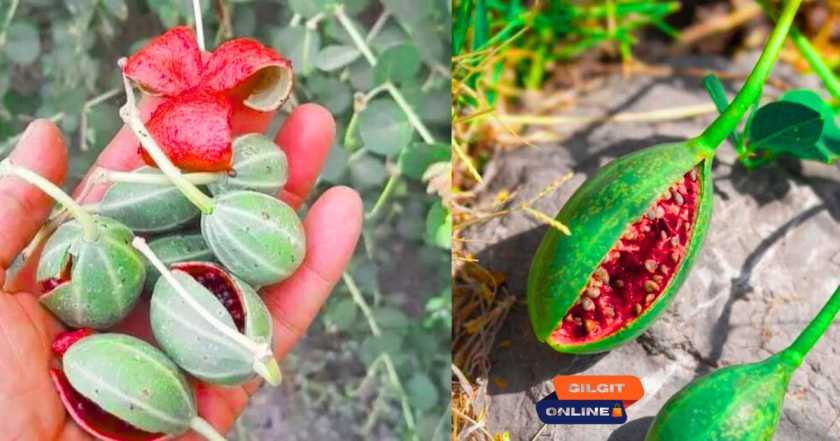

What is Capparis spinosa?
Capparis spinosa is a thorny shrub that produces flower buds (capers) and berry-like fruits (caper berries). The plant is highly drought-resistant and grows in rocky, arid climates, including the Himalayas, Mediterranean, and Middle East.
Key Features of Himalayan Capparis spinosa
| Leaves: Thick, rounded, and waxy (helps retain moisture). |
| Flowers: White-pink with long purple stamens. |
| Edible Parts: Flower buds (capers), fruits (caper berries), and young shoots. |
| Adaptation: Thrives in harsh, high-altitude conditions (up to 3,000 meters). |
Nutritional & Medicinal Benefits of Capparis spinosa
Capers and caper berries are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and bioactive compounds. Here’s why they’re beneficial:
1. High in Antioxidants
- Contains quercetin, rutin, and kaempferol, which fight oxidative stress.
- Helps reduce inflammation and may lower cancer risk.
2. Supports Digestive Health
- Traditionally used to treat indigestion, bloating, and constipation.
- Stimulates liver function, aiding detoxification.
3. Anti-Diabetic Properties
- Studies suggest it helps regulate blood sugar levels.
- May improve insulin sensitivity.
4. Boosts Heart Health
- Lowers LDL cholesterol and supports blood vessel function.
- Contains compounds that may reduce hypertension.
5. Anti-Arthritic & Pain Relief
- Used in Ayurveda and traditional medicine for joint pain relief.
- Reduces inflammation in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
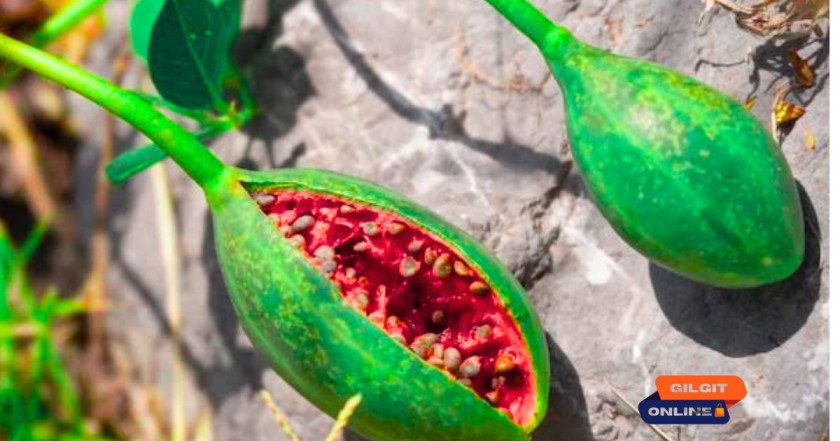

Culinary Uses of Capers & Caper Berries
Capers are a staple in Mediterranean cuisine, but Himalayan capers have a unique, slightly bitter taste.
How Are Capers Used in Cooking?
✔ Pickled Capers: Added to salads, pasta, and sauces (like tartar sauce).
✔ Caper Berries: Eaten as a brined snack or in antipasti platters.
✔ Seasoning: Provides a tangy, salty flavor to meats and fish dishes.
Popular Dishes Featuring Capers:
- Pasta Puttanesca (Italian)
- Salmon with Lemon-Caper Sauce
- Greek Salad with Capers
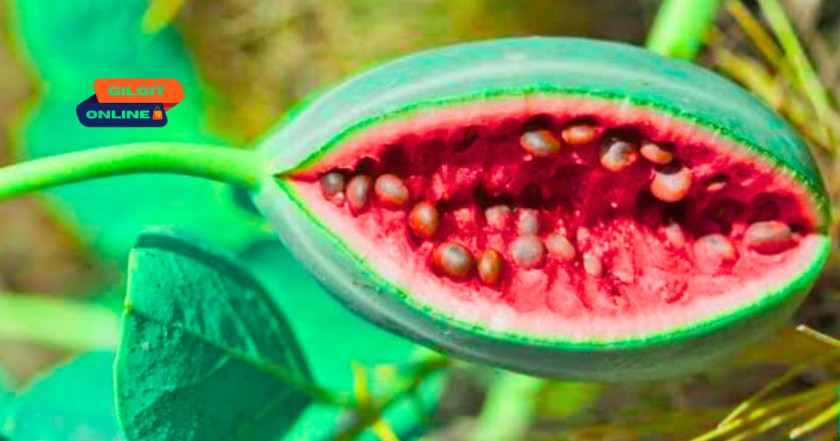

How to Grow Himalayan Capparis spinosa
Growing Capparis spinosa in your garden is rewarding but requires patience. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Climate & Soil Requirements
- Best for USDA Zones 8-10 (or indoors in colder regions).
- Soil: Well-drained, sandy/rocky soil (pH 6-8).
- Sunlight: Full sun (6-8 hours daily).
2. Planting & Propagation
- Seeds: Soak for 24 hours before planting (slow germination).
- Cuttings: Faster method—take semi-hardwood cuttings in spring.
- Spacing: Plant 3-4 feet apart (mature bushes spread widely).
3. Care & Maintenance
- Watering: Drought-tolerant—water sparingly (overwatering kills roots).
- Pruning: Remove dead branches to encourage growth.
- Pests: Resistant to most pests but watch for aphids.
4. Harvesting Capers
- Buds: Pick small, unopened buds (best for pickling).
- Berries: Harvest when plump and green-yellow.
Traditional Uses in Ayurveda & Folk Medicine
In Himalayan and Ayurvedic traditions, Capparis spinosa is called “Himsra” or “Kabra” and is used for:
- Liver detoxification
- Treating skin diseases
- Relieving rheumatic pain
- Boosting immunity
Home Remedy for Joint Pain:
- Caper root paste mixed with mustard oil is applied to swollen joints.
Where to find Capparis spinosa?